2021. 5. 23. 04:15ㆍ카테고리 없음
This is a tutorial on How to Configure OpenSSH on CentOS 7. Secure Shell or SSH is a protocol which allows users to connect to a remote system using a client-server architecture. The login session is encrypted and very secure. Today we are going to show you how to configure and use OpenSSH on a Linux VPS using CentOS 7 as an operating system. Configuring OpenSSH on CentOS 7 is a fairly easy task if you carefully follow the tutorial below.
CentOS 7 provides,opensshopenssh-server and openssh-clients packages. The openssh package requires openssl-libs to be installed on the system since it provides some very important cryptographic libraries.
- Centos 7 Ifconfig Not Found
- Install Telnet Client In Centos 7 Ifconfig Install
- Ifconfig Command Not Found Centos 7
- Centos Install Telnet Client
If you order a CentOS VPS Hosting with us you will have all these packages installed on your server. If not, you will need to install them manually.
For that purpose you can use the following command:
Installing Telnet Server in Centos /RedHat Linux. By default RHEL does not install Telnet Server in standard installation. To find out whether the Telnet Sever is installed or not we can use following rpm query command. Rpm –qa telnet-server. If above command does not return any output then telnet-server is not installed. # yum install telnet-server telnetRed Hat enterprise. Telnet to server (How do I use telnet client?). The author is the creator of nixCraft and a seasoned.
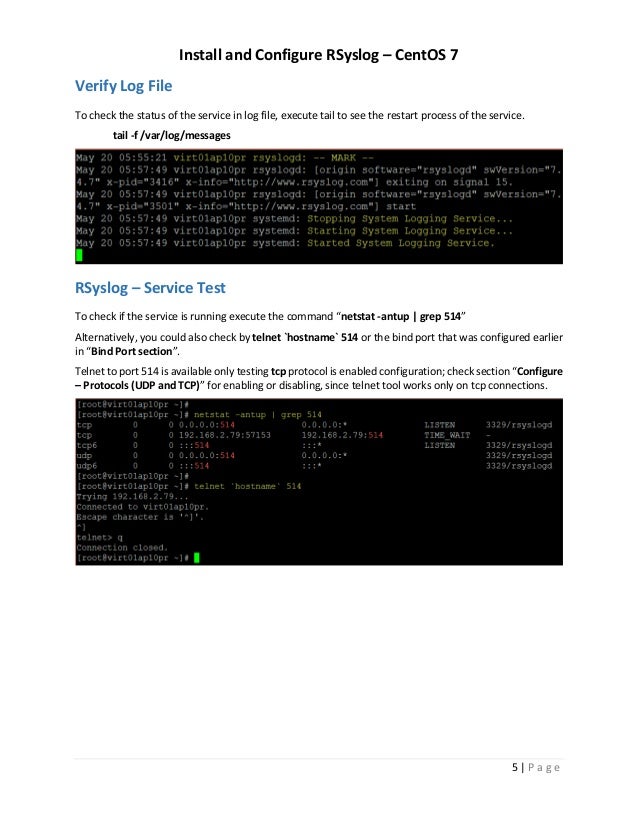
Once the packages are installed you are ready to connect to the server via SSH. The default configuration file for the sshd daemon is /etc/ssh/sshd_config and most of the settings for the daemon are defined in this file. Before making any changes, it is recommended to make a copy of the original configuration file so if you experience some problem you can revert the changes back the default.
Step 4: Enable the IPTables Firewall. By default, the active firewall application on a newly activated CentOS 7 server is FirewallD. Though it is a good replacement for IPTables, many security applications still do not have support for it. So if you'll be using any of those applications, like OSSEC HIDS, it's best to disable/uninstall FirewallD. First, let us see how to install and configure DHCP server on CentOS 7 64bit. The should also work on CentOS 6.x and other older versions. Install DHCP server and client using the below command.
To view and edit the configuration file you can use a text editor of your choice. We are going to use nano because of its simplicity.
The first thing you might like to change is the listening port number. By default, the SSH daemon listens on port 22 and for security reasons you can change the number to something else. Change the line:
to
You can use a port number of your choice which is not used by some other service on your CentOS VPS. Once you make the changes you can save and close the file. In order for the changes to take effect, you should restart the SSH daemon.
To improve security even further, it is recommended to use key-based authentication. Key-based authentication will allow you to connect to your server via SSH without using the password of your system user. Instead, you will need to use SSH keys. For more information about how to log in via SSH without password using SSH keys we recommend you to read our dedicated tutorial.
The SSH protocol allows other operations like copying files between two remote hosts to be completed in an encrypted and secure way. For that reason, you can use,scp a remote file copy program, and sftp which is an interactive file transfer program very similar to FTP. For more information on how to use scp and sftp you can read the user manual which is available at http://www.openssh.com/manual.html. We will cover this topic in some of our next Linux based tutorials.
Of course, you don’t have to know how to configure and use OpenSSH on CentOS 7 if you use one of our CentOS 7 VPS hosting services, in which case you can simply ask our expert Linux admins to help you with the OpenSSH configuration and setup on CentOS 7. They are available 24×7 and will take care of your request immediately.
PS. If you liked this post on how to configure OpenSSH on CentOS 7, please share it with your friends on the social networks using the buttons on the left or simply leave a reply below. Thanks.
Disclaimer:
Before installing and using Telnet, keep the following in mind.
- Using Telnet in public network(WAN) is very very bad idea. It transmits login data in the clear format. Everything will be sent in plain text.
- If you still need Telnet, It is highly recommended use it in the local area network only.
- Alternatively, you can use SSH. But make sure you’ve disabled root login in SSH.
Centos 7 Ifconfig Not Found
What Is Telnet?
Telnet is a network protocol which is used to connect to remote computers over TCP/IP network. Once you establish a connection to the remote computer, it becomes a virtual terminal and will allow you to communicate with the remote host from your local system.
In this brief tutorial, let us see how to install Telnet, and how to access remote systems via Telnet.
Installation
Open your terminal and type the following command to install telnet:
Now, the telnet has been installed in your server. Next, edit the telnet configuration file /etc/xinetd.d/telnet;
Set disable = no:
Save and quit the file. Be mindful that you don’t have do this step in CentOS 7.
Now restart the telnet service using the following command:
On CentOS 6.x systems:
Make this service to start automatically on every reboot:
On CentOS 6:
On CentOS 7:
Allow the telnet default port 23 through your firewall and Router. To allow the telnet port through firewall, Edit file /etc/sysconfig/iptables on CentOS 6.x systems:
Add the line as shown in red color:
Save and exit the file. Restart iptables service:
On CentOS 7, run the following commands to enable telnet service through firewall.
Thats it. Now telnet server is ready to use.
Creating users
Create a test user, for example “sk” with password “centos“:
Client Side Configuration
Install telnet package:
On DEB based systems:
Now, open Terminal, and try to access your server(remote host).
If your client is Linux system, open the terminal and type the following command to connect to telnet server.
Enter username and password which we have created in the server:
Sample output:
Install Telnet Client In Centos 7 Ifconfig Install
As you see in the above output, the remote system has been successfully accessed from the local machine.
If your client is windows system, then go to Start -> Run -> Command Prompt.
In the command prompt, type the command:
Where 192.168.1.150 is remote host IP address.
Now you will be able to connect to your server.
Ifconfig Command Not Found Centos 7
That’s it.
Centos Install Telnet Client
Cheers!